Unlock IoT Potential: Remote SSH On Ubuntu Made Easy!
Stuck managing your scattered IoT devices? It doesn't have to be a logistical nightmare. Embrace remote IoT web SSH download on Ubuntu it's the definitive solution for seamless, secure device management from anywhere with an internet connection. This opens the door to efficient management, eliminating the need for constant physical presence.
Remote management of IoT devices can often feel like navigating a complex maze. However, with the right tools and the proper knowledge, it transforms into a manageable task. Ubuntu, renowned for its robust SSH capabilities, emerges as a powerful platform for executing these operations efficiently and securely. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting your journey in the IoT landscape, this guide will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, illuminating every step of the process to effectively manage your remote IoT devices using SSH on Ubuntu.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Concept | Remote IoT Management |
| Technology | Web SSH on Ubuntu |
| Primary Use | Secure Remote Device Access |
| Benefits | Cost reduction, improved response time, enhanced security |
| Reference | Ubuntu IoT Official Website |
Remote IoT web SSH download on Ubuntu allows a secure connection to your IoT devices over the internet using SSH (Secure Shell) protocol. SSH ensures encrypted communication, safeguarding your data from unauthorized access. Ubuntus user-friendliness, coupled with its robust package management, simplifies the installation and configuration of SSH. Further, its expansive community and extensive documentation offer abundant resources for resolving any issues.
- Mydesinet Your South Asian Entertainment Gateway Guide
- Camilla Arajo Leaks The Untold Story Whats Next
To further clarify, IoT (Internet of Things) encompasses a network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity features, enabling them to exchange data. SSH, a cryptographic network protocol, ensures secure communication over unsecured networks. The synergy of these two technologies unlocks unprecedented possibilities for remote device management and control. In essence, it allows for the operation, monitoring, and maintenance of distant devices as if they were directly in front of you.
Remote access is vital for IoT projects, especially for devices in remote locations. With remote IoT web SSH download on Ubuntu, routine tasks such as firmware updates and troubleshooting can be done from anywhere. This capability significantly reduces operational overhead, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming on-site visits. The ability to diagnose and resolve issues remotely also minimizes downtime, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery.
Ubuntu is preferred by many IoT developers due to its stability, security, and ease of use. Its an ideal platform for running IoT applications, providing compatibility with a wide array of hardware. Its robust nature ensures you can deploy your solutions on virtually any device, making it a versatile choice for diverse IoT projects.
- The Price Of Betrayal Exploring A House Built On Tears Today
- Fikfap The Tiktok Porn App You Need Find Out Here
Several reasons contribute to Ubuntus prominence in the IoT space. Ubuntu boasts rock-solid stability, making it suitable for mission-critical IoT applications. With built-in security features and regular updates, Ubuntu ensures devices remain protected against potential threats, reducing the risk of breaches and vulnerabilities. The large Ubuntu community provides support through forums, documentation, and third-party tools, facilitating troubleshooting and collaborative problem-solving.
Ubuntu offers several features for IoT development. Ubuntu Core, a minimal version of Ubuntu, is designed for IoT devices, ensuring resource-constrained devices run efficiently. The apt package manager streamlines the development process, making it easier to install and manage software packages. Ubuntu's snap package format allows for easy distribution and installation of applications, ensuring IoT devices always have the latest software, automatically updated and managed.
Setting up SSH on Ubuntu is straightforward. First, install the SSH server on your Ubuntu machine by opening a terminal and running the command: sudo apt update && sudo apt install openssh-server. This command updates the package list and installs the OpenSSH server, the most widely used SSH server implementation, providing a secure channel for remote access.
Once installed, configure the SSH server to suit your needs. The main configuration file for SSH is located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Open this file using a text editor with the command: sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Modify settings such as the port number, login requirements, and encryption algorithms. After making changes, restart the SSH service with: sudo systemctl restart ssh. These modifications enhance the security and efficiency of your SSH connection.
To test the SSH connection, open a terminal on another machine and run the command: ssh username@your-ubuntu-ip-address. If the setup is correct, you should be able to log in to your Ubuntu machine securely. This step verifies that the SSH service is functioning as expected, enabling remote access to your device.
Security should be a priority when dealing with remote connections. Ensure SSH users have strong, unique passwords to prevent unauthorized access, thus reducing the risk of brute-force attacks. Disable root login via SSH to reduce the risk of brute-force attacks, adding another layer of security to your system. Instead of passwords, use SSH keys for authentication. This method is more secure and convenient, enhancing the overall security posture.
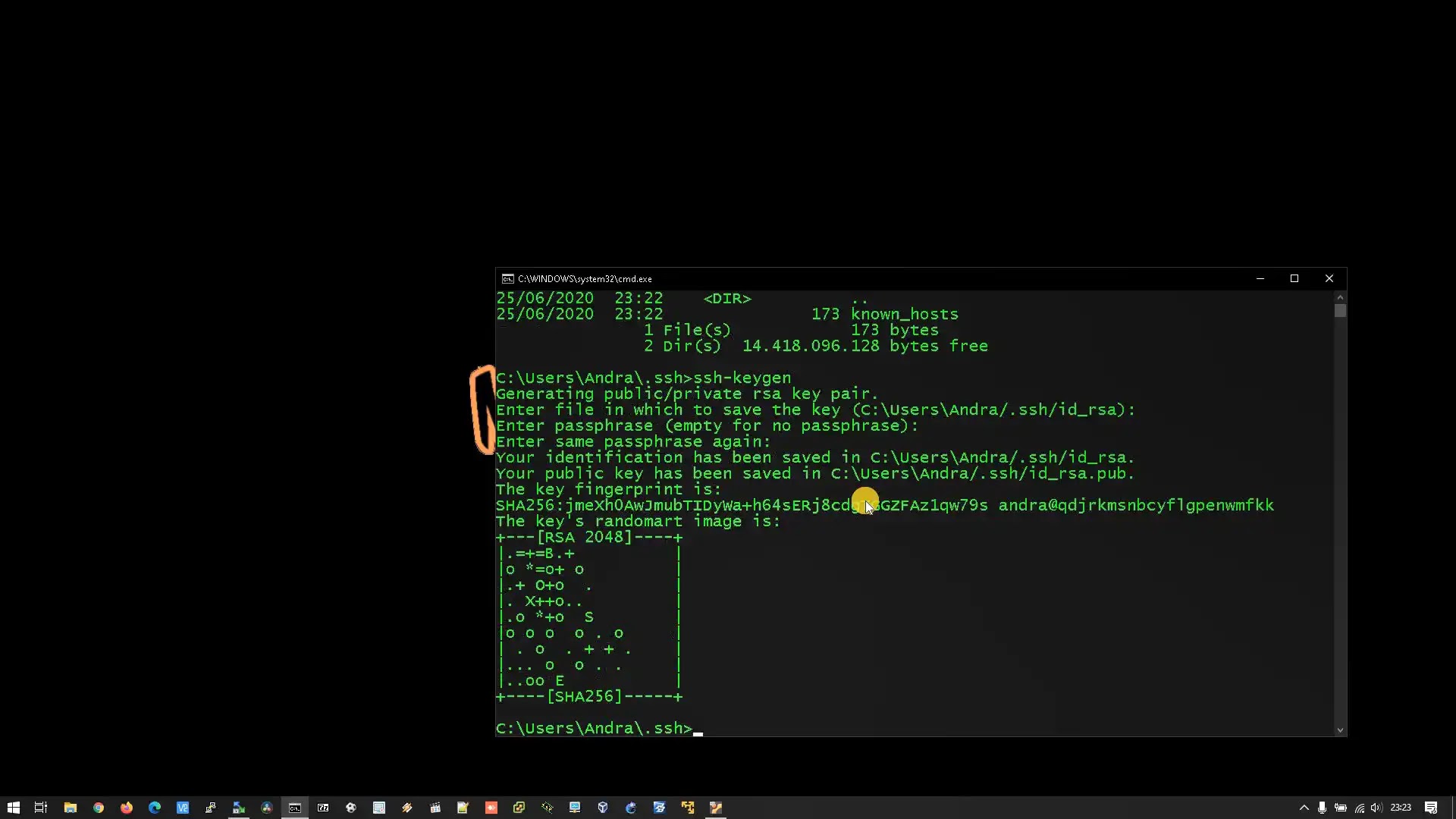
Generating SSH keys is simple. Run the command ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com" to generate a key pair. Follow the prompts to specify a file location and passphrase, providing an additional layer of security. Copy the public key to the remote server using the command ssh-copy-id username@your-ubuntu-ip-address. This enables key-based authentication, streamlining the login process while maintaining security.
With your secure SSH setup functional, you can start accessing IoT devices remotely, allowing you to manage devices, update firmware, and troubleshoot issues without physical presence. SSH provides a powerful command-line interface for managing IoT devices. Use SCP or SFTP to transfer files between your local machine and the remote device, enabling efficient data management. Monitor and manage processes running on your IoT device, allowing you to control and optimize device performance. Keep your device's software up to date by running apt update and apt upgrade, ensuring security and stability.
While traditional SSH clients work effectively, you might sometimes want to access devices through a web browser. Web-based SSH solutions provide a convenient way to manage IoT devices from any device with a browser, eliminating the need for dedicated SSH client software. Tools like Gate One, a web-based terminal emulator supporting SSH and Telnet, WebSSH2, a lightweight web-based SSH client requiring no installation, and TinyShell, a simple yet effective web-based SSH client, are all excellent solutions.
Downloading files from IoT devices is a common task when working remotely. SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) allows you to securely transfer files between your local machine and the remote device. Use the command scp username@your-ubuntu-ip-address:/path/to/remote/file /path/to/local/directory for file transfers. SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) provides a more interactive way to transfer files. Use it by running the command sftp username@your-ubuntu-ip-address, and then use commands like get and put to transfer files, providing granular control over file transfers.
Even with the best setup, issues can arise. If you encounter a "Connection Refused" error, ensure that the SSH service is running and that the firewall allows incoming connections on the specified port. Double-check your username, password, and SSH keys if you experience "Authentication Failed" errors. Make sure that the correct keys are installed on the remote server. For "Timeout Errors," increase the timeout settings in your SSH configuration or check your network connection to ensure stability. These steps are critical for maintaining a reliable connection.
To ensure a smooth and secure experience, follow these best practices. Regularly update your Ubuntu machine and all installed software to protect against vulnerabilities. Regularly check your SSH logs for any suspicious activity. Configure a firewall to restrict access to your SSH server only to trusted IP addresses, limiting exposure to potential threats. These practices significantly enhance the security and reliability of your remote connections.
- Fry99 Your Ultimate Guide To Online Gaming Entertainment
- Pinayflix Your Guide To Filipino Streaming Entertainment

SSH on Ubuntu Server blnLabs

How To Securely Connect Remote IoT Devices Using P2P SSH On Ubuntu
How to remote SSH to Ubuntu Server 20.04 root Without Password Using